Autistic children often experience social interactions differently, processing social cues and conventions in unique ways and struggling with the basic social skills many of us take for granted. This blog explores how social deficits can affect their daily lives, from communication struggles to peer interactions, and steps parents and caregivers can take to help their children develop essential social skills.

Understanding Social Skills Deficits in Autistic Children
Parents and caregivers often notice the first signs of autism when they’re observing how their child interacts with others. A deficit in social communication is one of the core symptoms that define autism spectrum disorder, and these autism signs can manifest in various ways, from how a child responds to their name to how they engage in play. In this blog, we look at what social deficits are, how they may impact the daily lives of autistic children, and a few ways that parents and caregivers can support their autistic children in becoming more comfortable and confident in social situations.
What Are Social Skills Deficits in Autistic Children?
To understand the challenges that autistic children (and adults) face in terms of social skills, we must first define what social skills are.
Social skills can be understood as the skills we use to communicate with the people we encounter daily. These include verbal and nonverbal communication methods, such as words and tone, gestures, and body language. More complex social skills also include understanding social norms, seeking social engagement, and understanding emotions. Social skills are important because they allow us to build and maintain relationships with others and communicate our needs, wants, and thoughts effectively. This can positively impact many areas of our lives, from career success and stress management to independence, conflict resolution, and even our emotional well-being.
However, autistic people often have certain social skills deficits, which means they may have significant challenges in developing or using these important social tools. That said, it’s important to note that autism presents differently in each person, so your autistic child may not display all (or even any) of these deficits. Some common examples of social skills deficits in autism include:
- Little to no interest in social interactions.
- Difficulty with listening and following conversations.
- Challenges in interpreting non-verbal cues like body language and facial expressions.
- Difficulty following instructions or directions.
- Speaking excessively during a conversation or interrupting frequently.
- Limited use of nonverbal social communication, such as pointing.
- Challenges with initiating or maintaining conversations.
- Difficulty empathizing and building rapport with others.
- Challenges in understanding or responding appropriately to the emotions of others.
- Taking everything said to them literally.
The Impact of a Lack of Social Skills
For an autistic child, a deficit in key social skills can have significant consequences that affect multiple areas of their lives. These consequences often include:
- Social rejection and isolation: Autistic children may find it hard to make friends or join in on group activities, often leading to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Academic struggles: Social skills are extremely important in a classroom setting. Without social skills, an autistic child may struggle to speak up in class, communicate with teachers and peers, or participate in group projects.
- Mental health challenges: The constant effort of navigating social situations can lead to increased anxiety, depression, stress, and sometimes aggression.
- Emotional development challenges: The ability to connect with others and understand social dynamics plays a significant role in emotional development. A lack of social skills can impact an autistic child’s self-esteem and self-awareness, making it harder for them to cope with emotions and build resilience.
- Physical health impacts: Stress and anxiety are known to cause several physical health issues, from gastrointestinal issues to sleep difficulties and other stress-related physical health problems. Autistic children with severe social deficits may also be less likely to engage in physical activities or sports, which can impact their overall physical health and development.
- Future opportunities and independence concerns: As children grow, social skills become increasingly important for navigating various aspects of life, including higher education and employment. Early social skills deficits can have long-term effects on the child’s ability to achieve independence and succeed in adulthood.
How To Help Autistic Children Who Lack Social Skills
The good news is that many aspects of social skills can be taught or improved. This can have numerous benefits for an autistic child, including lower stress levels, better outcomes, a stronger social network, and more success throughout their life.
Here are some tips to help improve social communication deficits in autistic children.
Lead by Example
As a parent, one of the easiest ways to help your child better understand how to interact with others is by leading by example. Your child will mimic you, including your social interactions, so being a good role model for your child will help them develop good social skills.
Roleplay
Is it your autistic child’s first day at school? Perhaps they’re going to a birthday party for the first time? Or maybe another child has just taken their favorite toy? Whatever the situation is, you can help your child be prepared by roleplaying both expected and unexpected events that may take place in their life.
Practice Using Toys and Games
Another important way for your child to improve their social skills is by using games that encourage the skills you want them to learn. For example, have a tea party with their stuffed animals and play out how the party should go with your child and their toys. A game that has turns, such as checkers or chess, is another great way to help your child understand the concept of taking turns with other people.
Encourage Interactions With Allistic Children
Whatever situation your autistic child is in, it’s important that you provide them with opportunities to engage with their allistic peers, either in a formal schooling environment or through specifically arranged events or playdates. Neurodiverse and neurotypical kids can learn a lot from each other, so getting them to socialize healthily can be a win-win.
Be On the Lookout for Buddy Programs
Your autistic child can also learn from people who are older than them but not necessarily adults. Some programs offer autistic children the chance to interact with older individuals who can act as mentors by helping autistic children learn and improve their social skills through various activities in the buddy program. This can be especially helpful if you can find an older neurodivergent person as a mentor — their lived experience will likely have equipped them with healthy coping strategies and techniques they can help your child with.
Praise Successful Social Interactions
If your autistic child has a positive interaction with a peer or adult, it’s important to let them know they did a good job. This will encourage them to interact positively with others in the future.
Specific Social Skills Lesson
If you are unable to assist your child yourself, it’s important that you enroll them in a school environment that provides them with specific social skills lessons or seek out the assistance of a specialist who can help them outside of a school setting. Many health professionals, including psychologists and occupational therapists, can assist you and your child with learning and improving their social interactions.
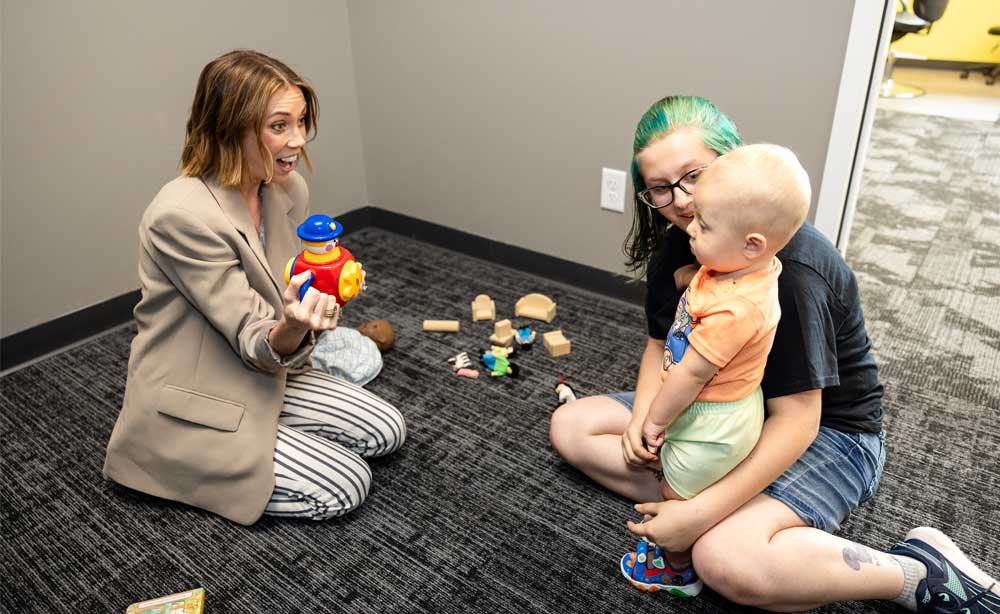
Discover How Lighthouse Autism Therapy Centers Can Help Your Autistic Child
At Lighthouse Autism Center, we provide a unique approach to ABA therapy that helps your child change, learn, or improve certain behaviors. This approach is known as Lighthouse Fusion® ABA therapy and combines ABA and speech therapy into an enhanced therapeutic program for autistic children. We also provide extensive autism resources to help you better understand autism, how it affects your child, and more.